Research
Optimization and Assessment of Digital Breast Tomosynthesis
Digital breast tomosynthesis is undergoing a continuous evolution, with special focus in new acquisition protocols that can enhance its clinical performance, reduce radiation dose to the patients and improve reading workflow, and in new processing algorithms that can optimize the quality of the images and the accuracy of radiologists’ interpreting them. Furthermore, the development of deep learning-based artificial intelligence has further expanded the possibilities for improving digital breast tomosynthesis. Deep learning algorithms are being developed not only for assisting the interpretation of breast images, but are also being investigated as methods to improve image quality and image reconstruction. In the AXTI group, we work in the aforementioned fields with the goal of clinical optimization of digital breast tomosynthesis, in order to assess and to increase its detection and diagnostic performance. We work closely with radiologists from Radboudumc and with experts from throughout the world, and we perform reader studies to determine what is the best way of using breast tomosynthesis in the clinic by analyzing different reading workflows as well as state-of-the-art reconstruction algorithms and by investigating the role of synthetic mammograms in clinical practice.
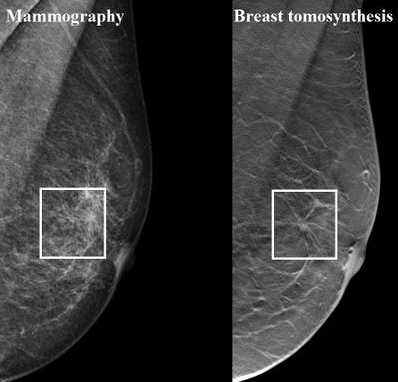
Visual comparison of breast lesion detection between traditional digital mammography and digital breast tomosynthesis.
Researchers:
Key Publications: