Research
Development of Physical Phantoms for Breast Dose Quality Control Procedures
For evaluation of breast dosimetry in quality control (QC) procedures in digital mammography (DM) and digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT), a practical and reproducible method using phantoms is required. Currently, this methodology utilizes slabs of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) to replicate the x-ray attenuation properties of an equivalent breast. However, the selection of exposure settings by modern automatic exposure control (AEC) sensors is based on more sophisticated processes. Thus, the simple homogeneous PMMA slabs approach is inappropriate to properly simulate the breast imaging systems as a real breast.

The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) and the European Federation of Organizations for Medical Physics (EFOMP) formed a joint Task Group/Workgroup (TG 323) which aims to develop a new breast phantom that adequately queries the response of the AEC mechanisms in a clinically realistic fashion. This project is therefore focused on combining breast feature characteristics (e.g. peak and mean density, fibroglandular volume, etc.) obtained from a large cohort of patients using commercial software (Volpara™) with the AEC functioning from all the major system manufacturers to develop the new phantom.
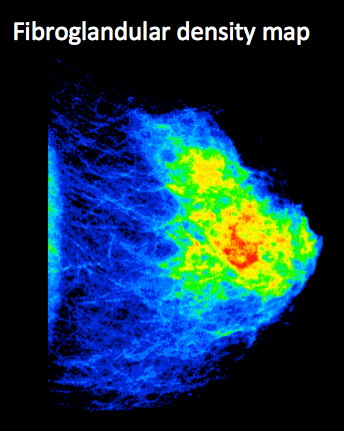
Example of fibroglandular density map obtained using a patient mammogram and used for the design of the phantoms.
Researchers: