Research
Development of a New Universal Breast Dosimetry Methodology
The joint AAPM/EFOMP Report 282 is out! Read all about it here.
Mammography is the reference technology for early detection of breast cancer; millions of women undergo mammography examinations every year both for screening and diagnosis. Being an x-ray imaging-based technique, characterization and optimization of the ionizing radiation dose delivered to patients is extremely important. Currently, the standard dosimetric quantity to evaluate the radiation dose in breast examinations is the average glandular dose (AGD). This quantity is based on several approximations that have been recently shown to significantly overestimate the amount of radiation dose resulting from mammography (e.g. the homogenous approximation of the internal adipose/glandular breast tissue mixture). Therefore, it is expected that a new breast model would overcome this limitation, involving a non-uniform and/or non-homogeneous tissue model. The American Association of Physicists in Medicine (AAPM) and the European Federation of Organizations for Medical Physics (EFOMP) formed a joint task group (TG 282), that aims to develop and disseminate a new model and corresponding methodology to estimate the AGD. In this project, a new model of fibroglandular tissue in the compressed breast is being developed, aiming to obtain better radiation dose estimates. Moreover, it is envisioned that this single new model will replace the current disparate methods used in the USA, Europe, and the rest of the world.
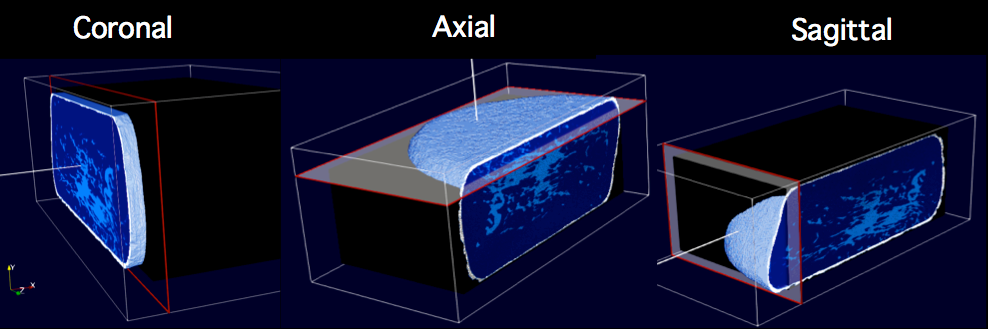
Automatic method for the identification of fibroglandular tissue patterns in a patient breast, used to calculate an accurate delivered radiation dose.
Researchers:
Key Publications:
- C. Fedon, M. Caballo, R. Longo, A. Trianni and I. Sechopoulos. "Internal breast dosimetry in mammography: Experimental methods and Monte Carlo validation with a monoenergetic x-ray beam.", 2018. Abstract. DOI.
- C. Fedon, M. Caballo and I. Sechopoulos. "Internal breast dosimetry in mammography: Monte Carlo validation in homogeneous and anthropomorphic breast phantoms with a clinical mammography system.", 2018. Abstract. DOI.
- C. Fedon, C. Rabin, M. Caballo, O. Diaz, E. García, A. Rodríguez-Ruiz, G. González-Sprinberg and I. Sechopoulos. "Monte Carlo study on optimal breast voxel resolution for dosimetry estimates in digital breast tomosynthesis.", 2018. Abstract. DOI.
- C. Fedon, L. Rigon, F. Arfelli, D. Dreossi, E. Quai, M. Tonutti, G. Tromba, M. Cova and R. Longo. "Dose and diagnostic performance comparison between phase-contrast mammography with synchrotron radiation and digital mammography: a clinical study report", 2018. Abstract.
- M. Masi, F. Di Lillo, G. Mettivier, A. Sarno, F. Arfelli, L. Brombal, S. Donato, C. Fedon, L. Rigon and P. Russo. "Dose monitoring in synchrotron radiation breast computed tomography with radiochromic films", 2018. DOI.
- A. Sarno, D. Dance, R. van Engen, K. Young, P. Russo, F. Di Lillo, G. Mettivier, K. Bliznakova, B. Fei and I. Sechopoulos. "A Monte Carlo model for mean glandular dose evaluation in spot compression mammography.", 2017. Abstract. DOI.
- D. Dance and I. Sechopoulos. "Dosimetry in x-ray-based breast imaging", 2016. Abstract. DOI.